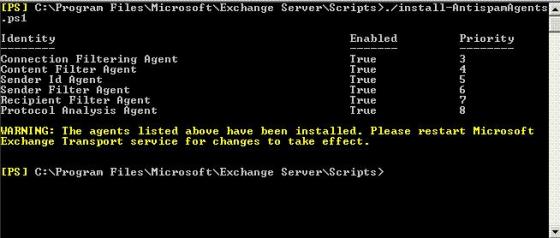
Below is the powershell command to export the complete details of the Mailbox in the Exchange Organization. Details like Name, Mailbox size (MB), Mailcount, Mailbox limits, Account Active or disabled, CreatedDate, Lastlogon time, Last logofftime etc into the CSV file. This Data can even imported in to the SQL database and Query to analyst the growth of the mailbox. If you collect these details on Daily basis and uploaded into SQL then you can easily get the details of the mailbox in seconds for auditing or capacity management etc.
With SQL integration you can query details like Top 100 mailbox, Top 100 Fastest growing mailbox, List of all active maibox, List of disabled mailbox, List of mailbox out of default quota limits, maiboxes not used in past few days. Newly created mailbox in past one month etc
Get-Mailbox -ResultSize Unlimited | select DisplayName, Alias, Database, PrimarySmtpAddress,@{name=’IssuewarningQuota’;expression={if ($_.IssueWarningQuota -match “UNLIMITED”) {“-1”} else {$_.IssueWarningQuota.value.tomb() }}},@{name=’ProhibitSendQuota’;expression={if ($_.ProhibitSendQuota -match “UNLIMITED”) {“-1”} else {$_.ProhibitSendQuota.value.tomb() }}},@{name=’ProhibitSendReceiveQuota’;expression={if ($_.ProhibitSendReceiveQuota -match “UNLIMITED”) {“-1”} else {$_.ProhibitSendReceiveQuota.value.tomb() }}},WhenCreated |export-csv C:\stats.csv
“DisplayName,Alias,MailboxSizeMB,ItemCount,PrimarysmtpAddress,IssueWarningQuotaMB,ProhibitSendQuotaMB,ProhibitSendReceiveQuotaMB,DatabaseName,CreationDate,LastLogonTime,LastLogoffTime,isActive” | out-file C:\MailstatsResult.csv
$csv = Import-csv -path “C:\stats.csv”
foreach($line in $csv)
{
$MailboxStats = Get-MailboxStatistics $Line.Alias | Select TotalItemSize,Itemcount,LastLogoffTime,LastLogonTime
$L = “{0:N0}” -f $mailboxstats.totalitemsize.value.toMB()
$Size = “”
$Len = $L.Split(‘,’)
for ($i=0; $i -lt $Len.length; $i++)
{
$Size = $Size +$Len[$i]
}
$temp=$Line.PrimarysmtpAddress
$adobjroot = [adsi]”
$objdisabsearcher = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher($adobjroot)
$objdisabsearcher.filter = “(&(objectCategory=Person)(objectClass=user)(mail= $Temp)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=2))”
$resultdisabaccn = $objdisabsearcher.findone() | select path
if($resultdisabaccn.path)
{
$actStatus = “1”
}
Else
{
$actStatus = “0”
}
$out =$Line.Displayname + “,” + $Line.Alias + “,” + $Size + “,” + $MailboxStats.ItemCount + “,” + $Line.PrimarySmtpAddress + “,” + $Line.IssueWarningQuota + “,” + $Line.ProhibitSendQuota + “,” + $Line.ProhibitSendReceiveQuota + “,” + $Line.Database + “,” + $Line.WhenCreated + “,” + $MailboxStats.LastLogonTime + “,” + $MailboxStats.LastLogoffTime + “,” + $actStatus
$Out | Out-File C:\MailstatsResult.csv -Append
}
You can get the copy of the script in the below text file
http://powershell.com/cs/cfs-filesystemfile.ashx/__key/CommunityServer.Components.UserFiles/00.00.00.30.62/MailboxStats.txt